No products in the cart.
No products in the cart.
Prostate health is a topic that affects millions of men worldwide but often goes undiscussed. The prostate, a small walnut-shaped gland located below the bladder, plays a crucial role in male reproductive and urinary health. Yet, as men age, the likelihood of encountering prostate-related issues increases significantly.
Early detection and preventive care are essential for maintaining prostate health. By understanding the common problems, recognizing symptoms, and exploring available treatments, men can take charge of their health and improve their quality of life.
The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system responsible for producing seminal fluid, which nourishes and transports sperm. It is located just below the bladder and surrounds the urethra. Although relatively small, the prostate’s function is vital for reproductive health.
Beyond its reproductive role, the prostate directly influences urinary health due to its position around the urethra. Changes in the prostate’s size or health can lead to significant urinary issues, impacting daily life and overall well-being.
BPH, or an enlarged prostate, is a non-cancerous condition where the prostate grows in size, often squeezing the urethra and causing urinary difficulties. This condition becomes increasingly common with age, affecting nearly 50% of men over 50 and up to 90% of men over 80.
Risk factors for BPH include age, hormonal imbalances, and genetic predisposition. While not life-threatening, the symptoms can significantly impact a man’s quality of life.
Prostatitis refers to inflammation of the prostate, which can be caused by bacterial infections or other factors. It is classified into acute, chronic, or asymptomatic forms. While acute prostatitis is often linked to bacterial infections and presents with severe symptoms, chronic prostatitis may develop without an obvious cause.
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers in men, with risks increasing significantly after the age of 50. Factors such as genetics, diet, and lifestyle play a role. While early stages of prostate cancer may not show symptoms, advanced cases can lead to severe complications if left untreated.
Men with BPH often experience urinary symptoms, including:
Prostatitis may present with:
Prostate cancer often progresses silently in its early stages, but symptoms in advanced stages may include:
A comprehensive medical history and a Digital Rectal Examination (DRE) are often the first steps in diagnosing prostate issues. While a DRE may feel invasive, it provides essential information about prostate size and abnormalities.
The Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) test measures PSA levels in the blood. Elevated PSA levels can indicate prostate issues, but it’s not a definitive diagnostic tool due to its sensitivity to various factors.
For a more detailed evaluation, imaging tests such as MRI or ultrasound, and sometimes a prostate biopsy, are utilized.

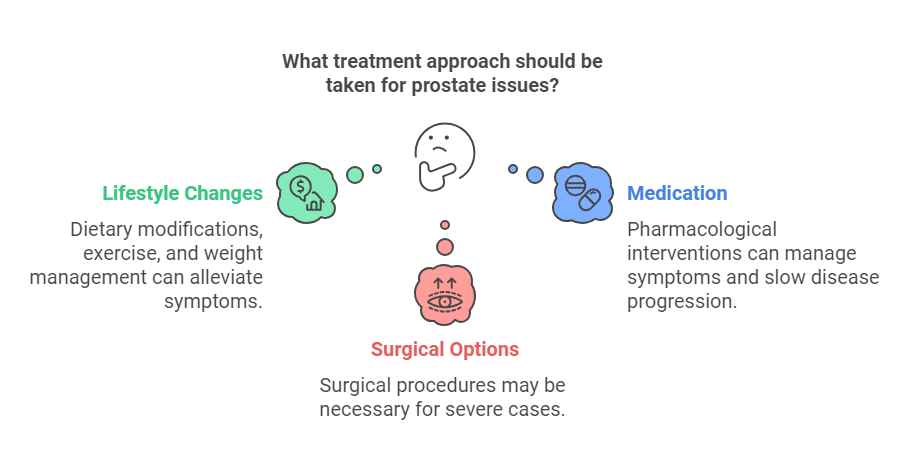
Antibiotics are the primary treatment for bacterial prostatitis, along with anti-inflammatory medications. Chronic cases may require a multi-disciplinary approach.
A well-balanced diet plays a crucial role in maintaining prostate health. Foods rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals can reduce inflammation and support cellular repair. Key dietary components include:
Avoiding processed foods, excessive red meat, and high-fat dairy can further protect against prostate problems.
Exercise is not just for maintaining a six-pack; it’s vital for prostate health too. Physical activity improves circulation, reduces inflammation, and supports hormonal balance. Activities like walking, jogging, or yoga can lower the risk of developing conditions like BPH and prostate cancer. Maintaining a healthy weight also minimizes the risk of obesity-related prostate issues.
Early detection saves lives. Routine prostate screenings, especially for men over 50 or those with a family history, are essential. Regular check-ups ensure that any potential issues are addressed before they escalate.
Living with prostate issues can be stressful, affecting emotional well-being and self-esteem. Men experiencing these conditions may face anxiety, depression, or even relationship challenges. Open communication with loved ones and professional counselling can make a significant difference.
Support groups for prostate health offer a sense of community and shared experiences. Remember, addressing emotional health is just as important as treating physical symptoms.
The medical field is continually evolving to improve prostate health outcomes. Exciting developments include:
Staying informed about these advancements can empower patients and provide hope for improved treatment outcomes.
Let’s bust some common myths about prostate health:
Prostate health is a critical yet often overlooked aspect of men’s overall well-being. Understanding the common problems, recognizing symptoms, and seeking timely treatment can dramatically improve outcomes. A proactive approach that includes a healthy diet, regular exercise, and routine screenings is key to maintaining prostate health and quality of life.
No matter your age, taking steps to care for your prostate today ensures a healthier tomorrow. Don’t shy away from discussing your concerns with a healthcare provider—your health is worth it.
1. What age should men start screening for prostate issues?
Most men should begin prostate screenings around age 50. However, those with a family history or other risk factors may need to start earlier, typically at 40–45.
2. Is prostate cancer always life-threatening?
No, prostate cancer is highly treatable when caught early. Many men live long, healthy lives after a diagnosis, especially with early intervention.
3. Can diet alone prevent prostate problems?
Diet plays a significant role, but it cannot prevent all prostate issues. A healthy lifestyle, including exercise and regular check-ups, is also crucial.
4. Are prostate problems hereditary?
Yes, a family history of prostate issues, particularly prostate cancer, increases your risk. Genetic testing and earlier screenings may help.
5. What is the outlook for prostate health in older men?
While prostate problems become more common with age, early detection and modern treatments ensure that many men maintain good health well into their senior years.
The content of this post is provided for informational purposes only. It is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional before making any decisions regarding your health or wellness. The author is not a licensed medical professional, and this information should not be considered medical advice.
If you need any further information or assistance with this article, don’t hesitate to Contact Us
Karen Blake
BAHN-NLP
TFT-DX



